Alimentary Canal

Alimentary Canal
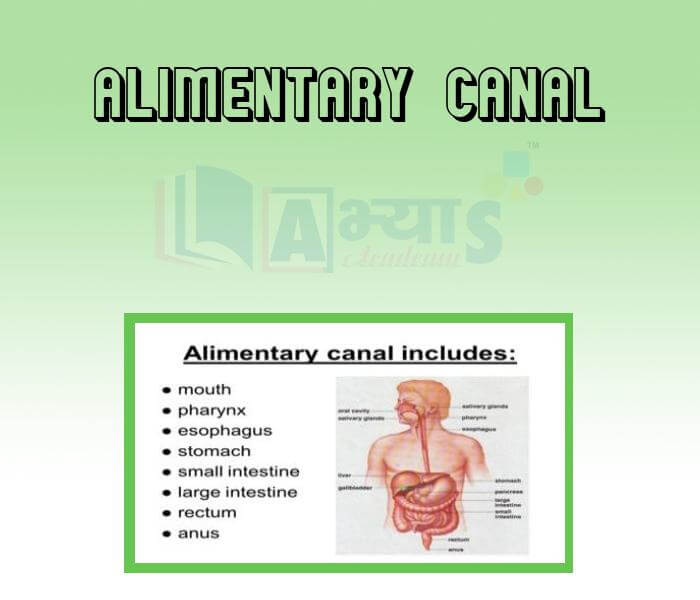
Alimentary Canal:
In human beings, the digestive system constitutes a long tubular structure called the alimentary canal which is about 7 - 8 metres long. It extends from the mouth to the anus. The complete process of ingestion, digestion, absorption, assimilation and egestion of food material is done within the alimentary canal itself. The alimentary canal can be divided into various components. Starting from mouth to anus, different parts of the canal can be written as :
1. Mouth : It is the starting point of our digestive tract. Food is ingested through mouth. About 30 % of carbohydrates get digested in the mouth. The mouth is filled with watery substance named as saliva. Saliva is consists of mucus, water and enzymes etc.
2. Oral Cavity : The oral cavity is consists of palate, tongue and teeth. Palate is the roof of the oral cavity. Tongue is the muscular and gladular structure attached to the base of the oral cavity.
3. Teeth are used for the mechanical churning of food. A tooth is white enamel below which dentine is present. Human are diphyodont i.e. they have two sets of teeth - milk or deciduous and permanent teeth. These are of four types incisors. canines, premolars and molars. In Humans, teeth are embedded in the sockets called as gums.
4. Pharynx : It is the common passage for food and air. Epiglottis prevents the entry of food into the windpipe.
5. Oesophagus : It is the muscular tube through which small bolus of food passes from the mouth to the stomach. The Gastro oesophageal sphinchter controls the movement of food into the stomach.
6. Stomach : It is a muscular bag, positioned at the upper left part of the abdominal cavity. It has four parts : cardiac,fundus, body and pyloric portion.
7. Small intestine : It is the longest part of the alimentary canal and comprises three parts - Duodenum, Jejunum and Ileum. It is the main site of digestion of food material.
8. Large Intestine :The small intestine leads into the large intestine. Rectum is the end point of large intestine.
9. Anus : It is the end point of alimentary canal. The undigested food get excreted out of the body through anus.
Which of the following is/are part of alimentary canal? | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which one is the widest part of alimentary canal ? | |||
| Right Option : C | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Which of the following are correct ? (a) In human beings, the digestive system constitutes a long tubular structure called the alimentary canal . (b) The oral cavity consists of palate, tongue and teeth. (c) Anus is the end point of alimentary canal. The undigested food get excreted out of the body through anus. | |||
| Right Option : D | |||
| View Explanation | |||
Students / Parents Reviews [10]
Abhyas is a complete education Institute. Here extreme care is taken by teacher with the help of regular exam. Extra classes also conducted by the institute, if the student is weak.

Om Umang
10thMy experience was very good with Abhyas academy. I am studying here from 6th class and I am satisfied by its results in my life. I improved a lot here ahead of school syllabus.

Ayan Ghosh
8thIt has a great methodology. Students here can get analysis to their test quickly.We can learn easily through PPTs and the testing methods are good. We know that where we have to practice

Barkha Arora
10thIt was good as the experience because as we had come here we had been improved in a such envirnment created here.Extra is taught which is beneficial for future.

Eshan Arora
8thOne of the best institutes to develope a child interest in studies.Provides SST and English knowledge also unlike other institutes. Teachers are co operative and friendly online tests andPPT develope practical knowledge also.

Aman Kumar Shrivastava
10thMy experience with Abhyas academy is very good. I did not think that my every subject coming here will be so strong. The main thing is that the online tests had made me learn here more things.

Hiya Gupta
8thAbhyas Methodology is very good. It is based on according to student and each child manages accordingly to its properly. Methodology has improved the abilities of students to shine them in future.

Manish Kumar
10thBeing a parent, I saw my daughter improvement in her studies by seeing a good result in all day to day compititive exam TMO, NSO, IEO etc and as well as studies. I have got a fruitful result from my daughter.

Prisha Gupta
8thIt was a good experience with Abhyas Academy. I even faced problems in starting but slowly and steadily overcomed. Especially reasoning classes helped me a lot.

Cheshta
10thMy experience with Abhyas is very good. I have learnt many things here like vedic maths and reasoning also. Teachers here first take our doubts and then there are assignments to verify our weak points.
